Dow Jones Industrial Average drops on fresh inflation, tariff, and recession fears
- The Dow Jones plummeted over 700 points on Friday.
- Investor sentiment is deteriorating after key PCE inflation metrics ticked higher.
- Ongoing tariff fears and souring consumer sentiment are also pushing stocks lower.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) backslid over 700 points on Friday, falling 1.75% and tumbling to 41,500 after core Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) inflation figures accelerated in February. Consumer inflation fears rose in March, and the consumer outlook on economic conditions also deteriorated further as tariff fears continue to take a bite out of general sentiment.
Core PCE Price Index inflation ticked up to 2.8% YoY in February as inflation pressures continue to flash warning signs that it will take longer for the Federal (Reserve) to achieve 2% inflation than previously thought. PCE inflation has functionally remained flat for a nine-month stretch, with monthly releases holding steady above 2.6% YoY since June of last year.
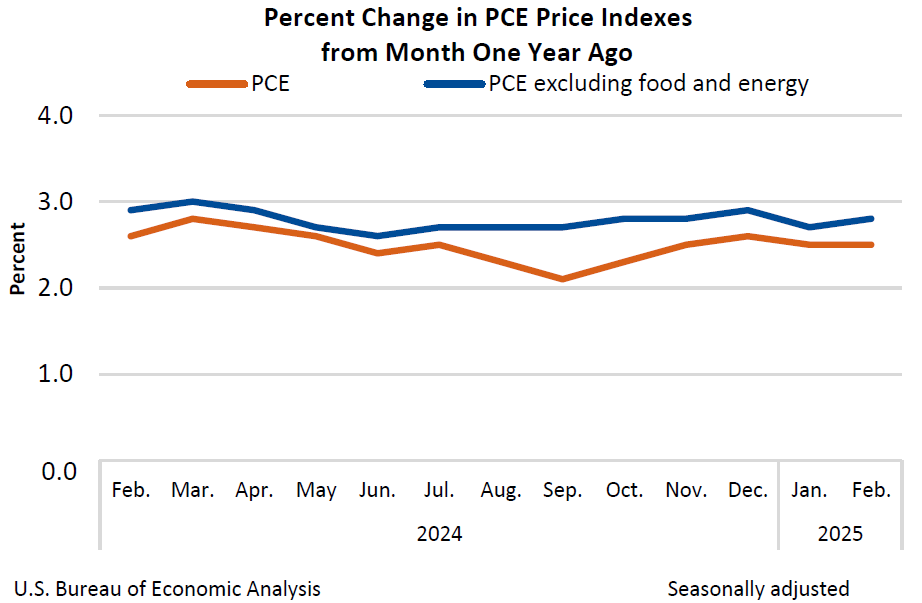
The University of Michigan (UoM) Consumer Sentiment Index crumpled to its lowest levels in over two years, falling to 57.0 compared to the expected flat hold at 57.9. UoM 1-year Consumer Inflation Expectations rose again, climbing to 5.0%. UoM Consumer 5-year Inflation Expectations also lifted to 4.1% versus the forecast of 3.9%. Median market forecasts widely expected consumer sentiment to remain flat in February as investors horribly misjudge how beleaguered US consumers are getting in the face of the Trump administration’s self-styled trade war. Despite President Donald Trump’s insistence that sweeping tariffs, set to take effect on April 2, will be good for the US, consumers are growing increasingly concerned that economic conditions are going to continue deteriorating and inflation will continue to rise.
President Trump reiterated on Friday that he will still enact a wide slew of tariffs on April 2, a day he continues to try and label Liberation Day. The Trump administration is promising to kick off a 25% tariff on all automobiles not produced in the US, as well as “reciprocal” tariffs on every country that has defensive tariffs on US goods. The Trump administration also plans to add further flat import taxes on items ranging from Copper, to microchips, and pharmaceuticals, as well as additional revenge tariffs of 20% on any country that also purchases Venezuelan Crude Oil.
Stock news
Equity indexes are down across the board on Friday. The Dow Jones fell over 700 points to 41,500, with the Standard & Poor’s 500 index backsliding 115 points to decline 2% on the day. The Nasdaq Composite tech index and shed weight, falling around 500 points to lose 2.7% from Friday’s opening bids.
Dow Jones price forecast
A fresh bout of selling has dragged the Dow Jones Industrial Average back below the 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near the 42,000 major handle. Price action is paring away recent gains after the Dow Jones’ last downturn, which dragged the index below 40,800.
The DJIA briefly recovered to the 42,800 region this week, but momentum has quickly turned lower once again, with the Dow Jones declining 3% top-to-bottom over a three-day period. Unless bullish momentum returns, the DJIA is poised for a fresh challenge of the 41,000 key level.
Dow Jones daily chart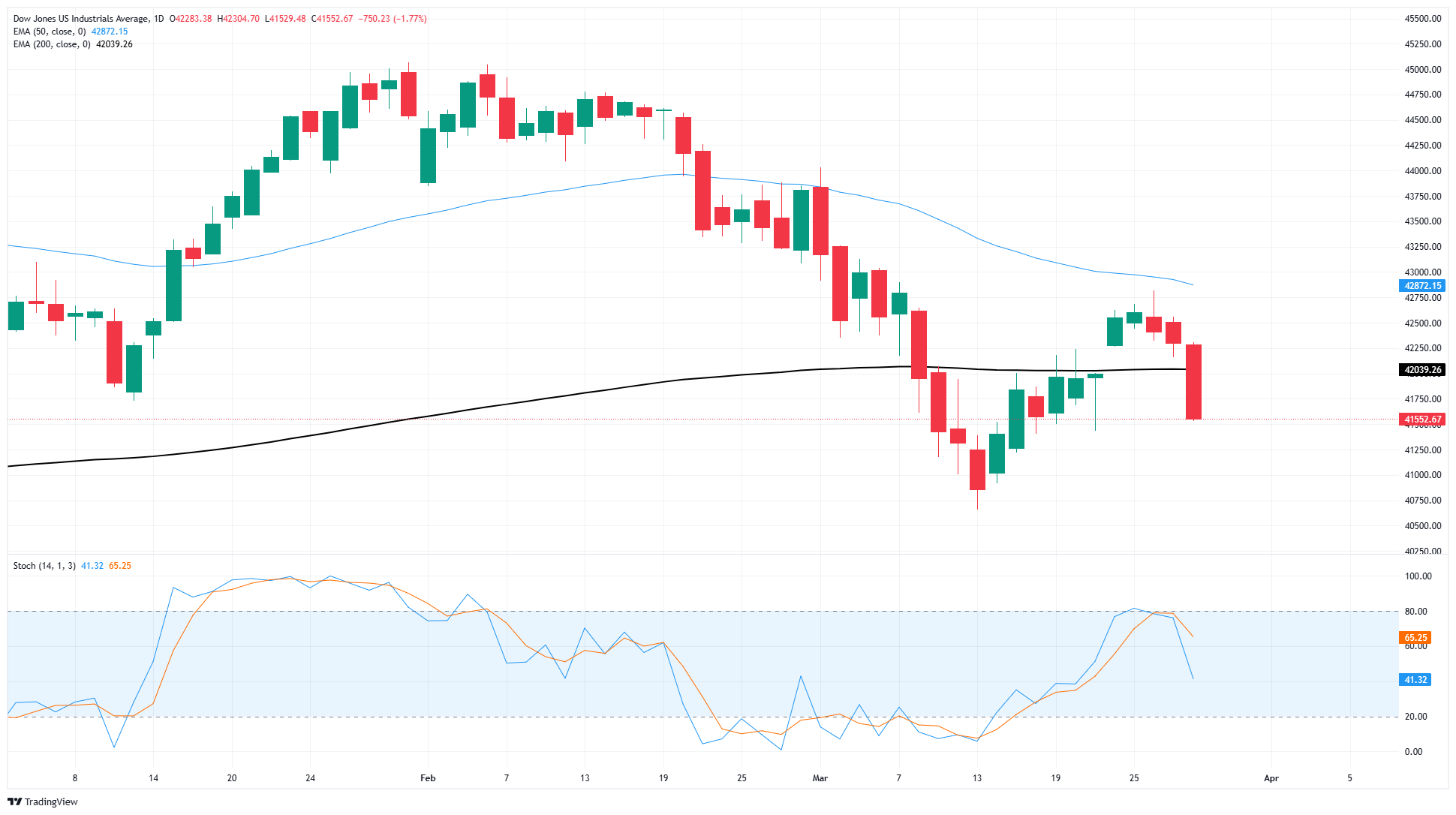
Dow Jones FAQs
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, one of the oldest stock market indices in the world, is compiled of the 30 most traded stocks in the US. The index is price-weighted rather than weighted by capitalization. It is calculated by summing the prices of the constituent stocks and dividing them by a factor, currently 0.152. The index was founded by Charles Dow, who also founded the Wall Street Journal. In later years it has been criticized for not being broadly representative enough because it only tracks 30 conglomerates, unlike broader indices such as the S&P 500.
Many different factors drive the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). The aggregate performance of the component companies revealed in quarterly company earnings reports is the main one. US and global macroeconomic data also contributes as it impacts on investor sentiment. The level of interest rates, set by the Federal Reserve (Fed), also influences the DJIA as it affects the cost of credit, on which many corporations are heavily reliant. Therefore, inflation can be a major driver as well as other metrics which impact the Fed decisions.
Dow Theory is a method for identifying the primary trend of the stock market developed by Charles Dow. A key step is to compare the direction of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) and only follow trends where both are moving in the same direction. Volume is a confirmatory criteria. The theory uses elements of peak and trough analysis. Dow’s theory posits three trend phases: accumulation, when smart money starts buying or selling; public participation, when the wider public joins in; and distribution, when the smart money exits.
There are a number of ways to trade the DJIA. One is to use ETFs which allow investors to trade the DJIA as a single security, rather than having to buy shares in all 30 constituent companies. A leading example is the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA). DJIA futures contracts enable traders to speculate on the future value of the index and Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the index at a predetermined price in the future. Mutual funds enable investors to buy a share of a diversified portfolio of DJIA stocks thus providing exposure to the overall index.
